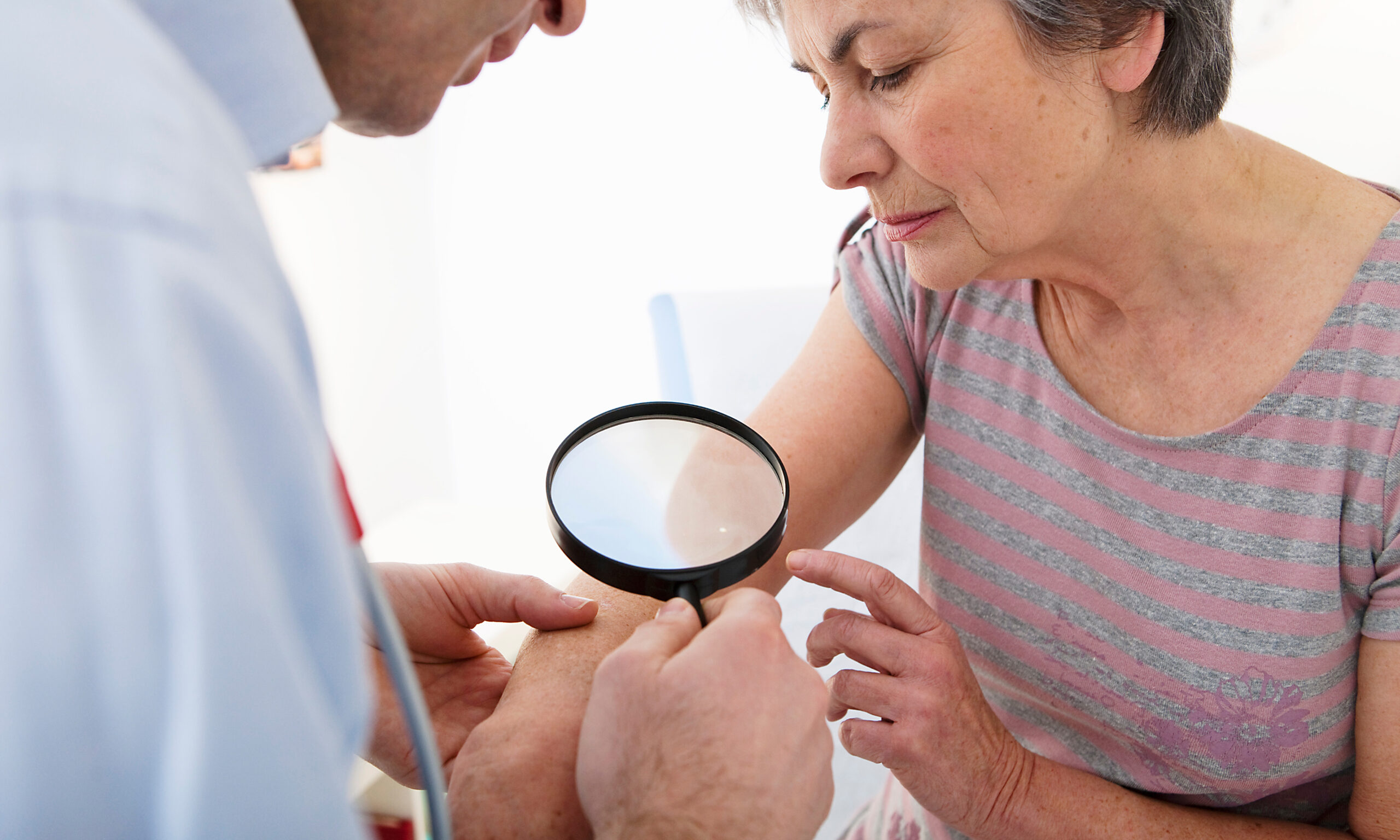
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States, with 1 in 5 people developing it before the age of 70. Early detection is critical to curing skin cancer, so if you are at risk or have symptoms of skin cancer, you should have a skin cancer screening.
What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is cancer that develops in the skin cells. The three most common types of skin cancer are:
- Basal cell carcinoma: Develops in the basal cells, which are the deepest part of the epidermis. This type of skin cancer is the most common, and is usually curable.
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Develops in the squamous cells, which are the thin cells that make up the outer layer of the skin. This type of cancer is also usually curable.
- Melanoma: The most serious form of skin cancer, it starts in the melanocytes, which make the pigment that gives your skin color. Melanoma can spread to other parts of the body, which is what makes it the most dangerous.
Symptoms of Skin Cancer
Symptoms of skin cancer depend on the type of skin cancer and may include:
- A rough patch on the skin that doesn’t go away
- A new growth that appears on the skin that may look like a mole, a bump, or a scab
- A sore that won’t heal
- Changes to an existing mole, such as changes in shape or color
- A skin growth that has itchiness or pain around it
Most skin cancers develop in areas that are exposed the most to sunlight, such as the face, lips, ears, scalp, arms, and the back of the hands. If you go the pool or lay out in the sun frequently, it can also appear on the legs, back, and stomach.
Some skin cancers can appear on areas of the body that are not exposed to sunlight. People with dark skin tend to get skin cancer in these unexposed areas.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Risk factors for skin cancer include:
- Ultraviolet light exposure from the sun or tanning beds
- History of sunburns
- Fair skin, light hair, green or blue eyes
- Freckles and moles
- Age – risk increases as you get older
- Family history
- A weakened immune system
- Certain medical conditions
- Exposure to chemicals, such as arsenic
What Happens During a Skin Cancer Screening?
During a skin cancer screening, the medical provider will examine all areas of your skin, particularly moles, to check for any abnormalities. If any are present, the doctor will excise, meaning to cut out, the area and send it to the lab for biopsy. A pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope, looking for cancer cells.
If you have any risk factors for skin cancer, you should have regular skin cancer screenings. Melanoma, in particular, should be detected as early as possible in order for it to be cured. Once it spreads, survival rates drop dramatically.
Treating Skin Cancer
Treatment for skin cancer depends on the type and stage of the cancer.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment
The most common treatment for basal cell carcinoma is surgery. The cancer may be removed by surgical excision, along with an area around the cancerous area which is then examined for cancer cells. Alternatively, for larger or deeper areas of cancer, the area is removed layer by layer. Each layer is examined for cancer cells, and layers continue to be removed until no cancer cells are left.
In other circumstances, or when surgery is not an option, other treatments may include:
- Curettage and electrodessication (C and E), where the surface of the area is removed and then the base is seared with an electric needle.
- Radiation therapy
- Freezing
- Topical treatments
- Photodynamic therapy, which uses photosensitizing drugs and light to treat the cancer.
In cases in which the cancer has spread, which is rare, targeted drug therapy or chemotherapy may be used.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Treatment for squamous cell carcinoma is similar to that of basal cell carcinoma. Treatments for small cancers include:
- Curettage and electrodessication (C and E)
- Laser therapy
- Freezing
- Photodynamic therapy
Larger squamous cell cancers may be treated with surgery or radiation therapy. If the cancer has spread, chemotherapy or targeted drug therapy may be used. In cases where the squamous cell carcinoma is advanced, immunotherapy may be used.
Melanoma Treatment
Treating melanoma starts with determining the stage of the melanoma. This is done by measuring the thickness of the melanoma, and testing the lymph nodes to see if the cancer has spread. If there is a concern that the melanoma has spread to other parts of the body, X-Rays, CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans may be performed.
Treatment for melanoma generally starts with surgery to remove it. For small, thin melanomas, surgery may be the only treatment needed. For more advanced melanoma, treatments include:
- Radiation therapy
- Targeted drug therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy
In Closing
If you have risk factors for skin cancer, regular skin cancer screenings are highly recommended. Even if you don’t have risk factors, a screening is still a good idea, particularly if you’ve noticed anything unusual on your skin. The team at Health Service Alliance is here to help if you need a skin cancer screening. We are dedicated to providing compassionate, personalized, and accessible care regardless of your ability to pay. Reach out today to learn more.