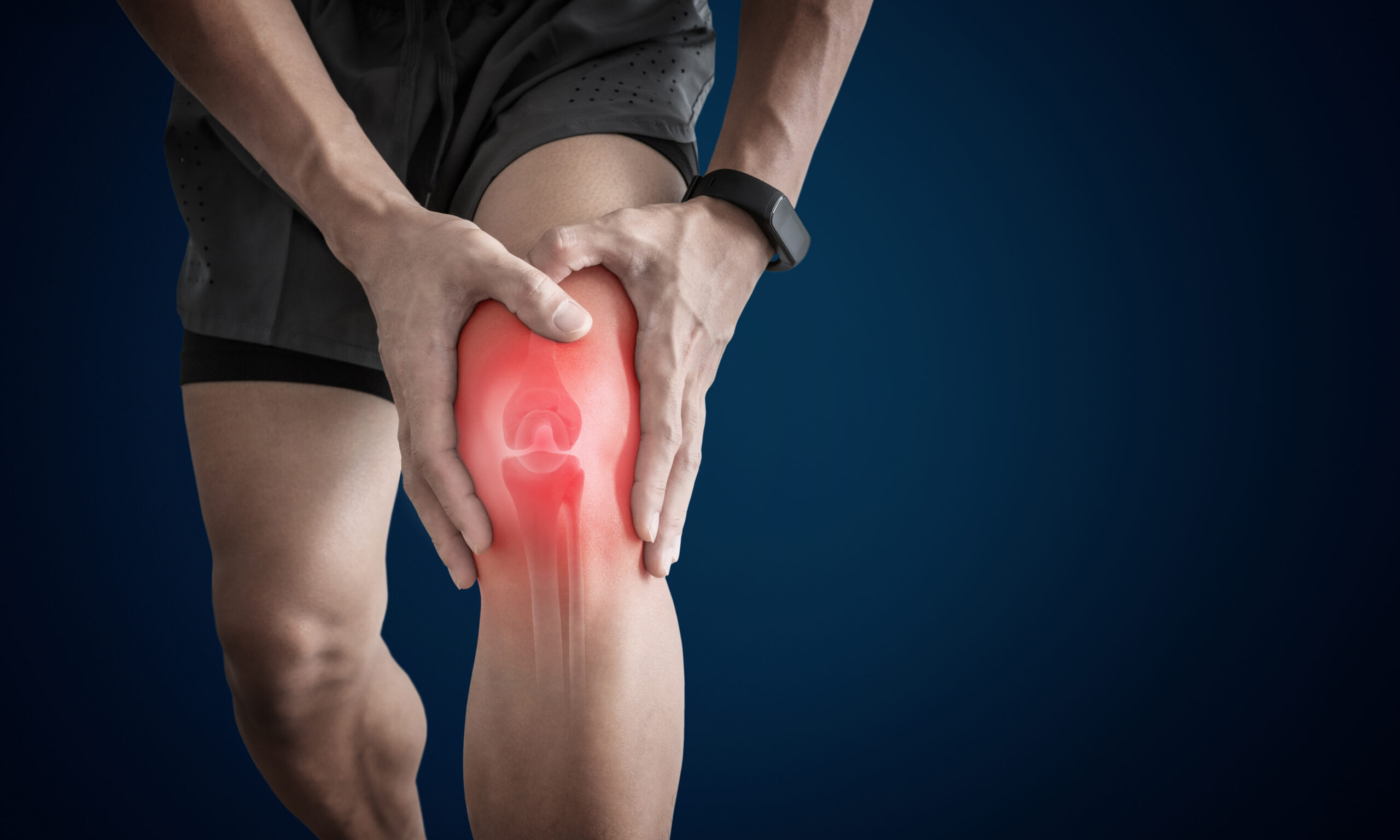
Arthritis is common, affecting about 1 in 5 people in the United States, and is characterized by joint pain and inflammation. It’s important to understand arthritis, how it develops, and how it is treated so that if you suffer from it, you know how to manage it.
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a disease that damages the joints, causing pain and stiffness. The most commonly affected joints are the:
- Hands and wrists
- Feet and ankles
- Knees
- Hips
- Shoulders
- Lower back
Types of Arthritis
There are many different types of arthritis, more than 100, but six are the most common.
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative type of arthritis where the cartilage in the joints wears down over time.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: A condition where the immune system incorrectly damages tissues in the body damaging the joints and bones. This can cause joints to bend and become deformed.
- Gout: Uric acid crystals form in the joints causing pain, swelling, and redness.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Arthritis affecting the spinal joints, usually in the lower back.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Arthritis that develops in those who have psoriasis.
- Juvenile Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder that affects children under 16.
Causes of Arthritis
The causes of arthritis depend on the type of arthritis.
Osteoarthritis is caused by normal wear and tear on the joints over time. Rheumatoid arthritis is caused by the immune system attacking the tissue in the joints. Genetic factors play a role in the development of some types of arthritis, but the causes of other types are largely unknown.
Risk Factors for Arthritis
Several risk factors contribute to the development of arthritis.
- Age: The risk of arthritis increases as you get older.
- Injuries: Injuries to the joints can cause arthritis to develop over time.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts stress on the joints, which can lead to the development of osteoarthritis
- Sedentary lifestyle: Joints weaken when you don’t get regular physical activity.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and joints, which can lead to rheumatoid arthritis.
- Diet: A poor diet high in processed foods, sugar, and red meat can cause inflammation which can affect the joints.
- Genetics and Family History
- Gender: Women are at higher risk than men.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups are at higher risk for arthritis.
- Autoimmune Disorders: People with psoriasis and lupus can develop arthritis.
- Hormonal Changes: Menopause and pregnancy hormonal changes can lead to the onset of arthritis.
- Exposure to Dust and Chemicals: Those who work at certain jobs, such as mining, are consistently exposed to dust and chemicals that can contribute to the development of arthritis.
Treatment for Arthritis
Arthritis treatments depend on the type and severity, and include medications, physical therapy, and surgery.
Medications
Common medications used for arthritis include:
- NSAIDs: Medications to relieve pain and inflammation. Examples include Ibuprofen and Motrin. These must be used with caution, however, because they can cause stomach irritation and lead to ulcers when overused.
- Counterirritants: Creams that contain menthol or capsaicin can relieve pain.
- Steroids: Pills or injections that reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and slow the progression of joint damage.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: Slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis.
Physical Therapy
In some cases, physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles around joints and increase range of motion. Splints or braces may also be helpful for some.
Surgery
When other treatments are ineffective, surgery may be recommended.
- Joint Repair: Joints can be smoothed or realigned to reduce pain. This type of repair is often done arthroscopically.
- Joint Replacement: Damaged joints can be replaced with artificial ones. This is most common for the knees and hips.
- Joint Fusion: The ends of both bones in the joint are removed and the bones are then fused together. This is most commonly done for fingers, wrists, and ankles.
Managing Arthritis with Lifestyle Changes
You can take control and make certain lifestyle changes that can help to manage your arthritis symptoms.
- Exercise: Regular light to moderate physical activity can help to strengthen the muscles around your joints and improve blood flow to your joints, which can promote joint regeneration. Exercise is also a natural mood booster, which can help to reduce your pain. Just be careful not to do physical activity that puts stress on your joints. Swimming is a good option, and yoga can also be very helpful. You can work with a physical therapist to put together an exercise plan that’s right for you.
- Diet: Eating a healthy diet that includes foods that have anti-inflammatory properties can help to reduce pain. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fatty fish like salmon or mackerel are good options. You should also eliminate processed foods and refined sugars, which can increase inflammation.
- Weight Loss: If you’re overweight, slimming down can reduce the stress on your joints.
- Stop Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow and slows healing processes, which can make your arthritis difficult to manage.
- Stress Management: Stress can manifest in physical pain, so try to keep your stress to a minimum. You can try meditation, breathing exercises, or yoga. Exercise can also reduce stress.
- Ergonomic Devices: Many devices exist that can help you reduce daily stress on your joints.
In Closing
Arthritis is common and can develop as you age. Its causes are not fully known, but if you suffer from it, it can be treated and managed. If you have arthritis, or suspect that you do, Health Service Alliance is here to help. We are dedicated to providing compassionate, personalized, and accessible care regardless of your ability to pay. Reach out today to learn more.